Blockchain technology is emerging as the ultimate weapon in the fight against cybercrime. It’s not only an innovative technology that revolutionizes the way we store and share data, but it’s also a powerful cybersecurity tool.
Blockchain provides a secure, transparent, and immutable platform for storing and sharing digital data. By leveraging the power of distributed ledger technology, organizations can ensure that their data are safe from manipulation, unauthorized access, and malicious attacks.
The explosion of online data in the information age has brought flaws in security protocols that regularly expose our most sensitive information to malicious actors. Thus, finding a reliable cybersecurity protocol is more crucial than ever.
Any attempt to gain unauthorized access to one or more computers with the intent to cause harm is a cyberattack. It attempts to disable computers, steal data, or use a breached computer system to launch further attacks.
In October 2020, Google released details of a pervious cyberattack launched against its servers in September 2017. The report describes the incident as a foreign-origin Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack that escalated over a six-month campaign. It was the largest attack of its kind on record.
The February 2020 DDoS attack against an Amazon Web Services (AWS) customer was the largest attack against AWS and to date one of the largest publicly disclosed attacks on anyone.
By 2025, researchers at Cybersecurity Ventures predict $10.5 trillion (about $32,000 per person in the US) in worldwide damages. Cyberattacks occur every 39 seconds and accumulate to 30,000 hacks per day.
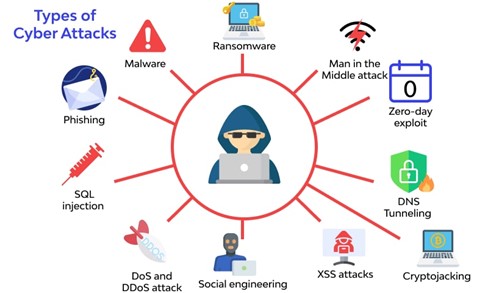
Common Types of Cyberattacks
Bad actors take advantage of the distributed nature of the Internet to maintain anonymity and overcome resistance to their attacks. A common DDoS method works by first infecting multiple nodes over a variety of domains to form a semi-coordinated network called a “Botnet”. These individual bots are hijacked to launch attacks against highly centralized targets, often giving hackers an asymmetric advantage.
More distributed software deployment, database management, and security protocols render targets less vulnerable by spreading out attack surfaces and relying on less centralized trust. The key to this decentralized approach may lie in a solution that already has multiple features that make it resilient to Blockchain attacks.
What Can Cyberattacks Do?
If successful, cyberattacks can damage enterprises. Cyberattacks can cause a wide range of harm, from disrupting services to stealing sensitive data. They can be used to take down websites, networks, and systems, as well as disrupt services and steal personal information. Cyberattacks can also be used to target critical infrastructure, leading to power outages, water contamination, and other damages. They can cause valuable downtime, data loss or manipulation, and money loss through ransoms. Further, downtime can lead to major service interruptions and financial losses, for example:
- DoS, DDoS, and malware attacks can cause system or server crashes
- DNS tunneling and SQL injection attacks can alter, delete, insert, or steal data from a system
- Phishing and zero-day exploit attacks allow attackers entry into a system to cause damage or steal valuable information
- Ransomware attacks can disable a system until the company pays the attacker a ransom

- Can a Blockchain strengthen the security of your solutions?
- Can we use potential Blockchain technology for securing data and communications?
- Can we use Blockchain capabilities for cybersecurity?
The answer to the above questions is in the affirmative. Blockchain technology offer important cybersecurity benefits, such as reducing cyberattacks, and it has created a lot of hype as a panacea for all the current challenges related to information security.
Why Blockchain Could Be a Solution for Cybersecurity?
Blockchain technology has several useful applications in the field of cybersecurity, such as:
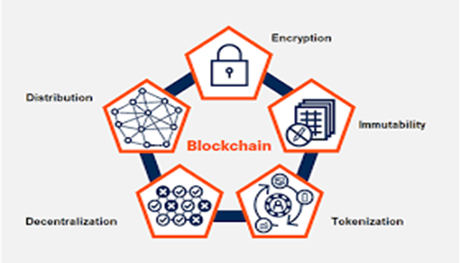
- Decentralized Security: Blockchain technology allows for the creation of decentralized security systems. By replicating data across multiple nodes on a network, it becomes more difficult for hackers to breach the system since they would need to compromise multiple nodes simultaneously. This is a powerful feature for securing data, systems, and applications.
- Immutable Records: The data stored on the Blockchain is immutable and cannot be modified or deleted once it is recorded. This feature can be leveraged to create tamper-proof audit trails and transaction logs. Using Blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or falsify data, which can be very useful in detecting and preventing fraud.
- Secure Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms of the agreement between the buyer and the seller are written directly into a line of code. Blockchain technology provides a secure platform for the deployment of smart contracts, which can be used to automate processes and eliminate the need for intermediaries.
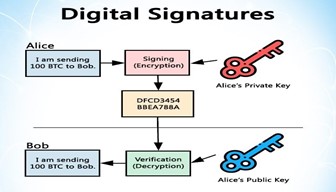
- Cryptographic Security: Blockchain technology relies on cryptographic algorithms to secure transactions and data. The use of cryptographic hashes and digital signatures help prevent data tampering and ensure the integrity of information stored on the Blockchain.
- Decentralized Identity Management: Blockchain technology can also be used to create decentralized identity management systems. Using Blockchain, individuals can control their identity information, reducing the risk of identity theft and other types of cyberattacks.
Overall, the combination of decentralized security, immutable records, secure smart contracts, cryptographic security, and decentralized identity management make Blockchain technology a valuable tool in the fight against cyber threats.
Blockchain technology can be used to prevent any data breach, identity theft, cyberattacks, or criminal acts in transactions.
This ensures that data remains private and secure. Indeed, it could improve cyber defense by being a platform for preventing fraudulent activities through consensus mechanisms.
Blockchain could also detect data falsification through its underlying characteristics such as operational resilience, data encryption, auditability, transparency, and immutability.
Key properties that make Blockchain far superior and better than the traditional system of information ledgering are as follows:
- Distributed shared ledger and immutable records
- Decentralized consensus mechanisms
- Smart contracts, cryptographic key pair, and peer-to-peer network
- Identity and access management with enhanced security
- Traceability and transparency in transactions
- No central authority or need for trusted third-party involvement
The Fundamentals of Blockchain Security
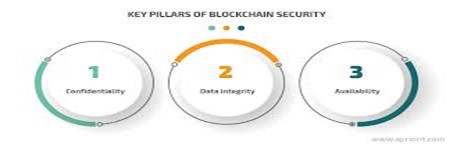
- Confidentiality: Blockchain provides extensive capabilities for ensuring a user’s anonymity. User keys are the only link between the user and his data. However, these keys are also easy to anonymize. As a result, while being open and offering rich opportunities for transaction tracking, Blockchain allows users to maintain an unprecedented level of anonymity.
- Data Integrity: Blockchains are designed as ledgers where every block is linked to nearby blocks using cryptographic hash functions. Therefore, once a transaction is recorded on the Blockchain, it can’t be altered or deleted. Any changes made to the already recorded data are processed as new transactions.
- Availability: Having many nodes ensures Blockchain resilience even when some nodes are unavailable. And as each node in the network has a copy of the distributed ledger, the correct Blockchain remains accessible to other peers even in the case of a compromised node.
What Are the Additional Levels of Security That Blockchain Is Offering?

- There are several types of access management systems, namely DAC, RBAC, and ABAC. Attribute-based Access Control (ABAC) can be re-envisioned for the future with a decision of user accessing transactions based on identification. The data stored and moved inside the blockchain-based solution is encrypted. It can be thus used to establish a stronger and more secure identity and access management.
- The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) paradigm is often recognized as a good security technique. Yet, it is based on a few identified challenges. A smart contract can be configured to invoke specific PKI operations, entities can have multiple attributes to authenticate using a public key/Ethereum address.
- Domain Name System (DNS) chain has emerged as a well-known initiative to alter the DNS infrastructure and secure it against spoofing attacks. It substitutes X.509 Certificates with MITM-resistant public key infra. This advocates the use of an Ethereum-based DNS network to connect clients and name servers rather than the centralization of the system root server. DDoS prevention services may also deploy a distributed ledger to blacklisted IPs at the same time, decreasing the danger of a single point of failure for the centralized web application layer.
- An Ethereum-based OTP generation that does not directly interact with the user app but is heavily restricted by a smart contract can be built.
How Does Blockchain Fight Cyber-Security Threats?
The powerful combination of HashCash and smart contracts offers a set of security tools that are distributed, peer-to-peer, cryptography-based, and often open-sourced.
- Preventing Data Manipulation: The combination of hashing and cryptography with the decentralized structure lends Blockchain its most powerful feature, like immutability. It helps protect data integrity and identify any type of data tampering. Keyless Signature Infrastructure (KSI) is a new technology developed by a company called Guardtime, which replaces the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). KSI adds authentication to the existing features of PKI.
- Protecting Identities: Publishing keys on Blockchain eliminates the risk of false key propagation and identity theft. Various projects are ongoing to eliminate the need for issuing certificates by central authorities. These advances have made Blockchain technology more robust in terms of authentication and elimination of any possibility of being a single point of failure.
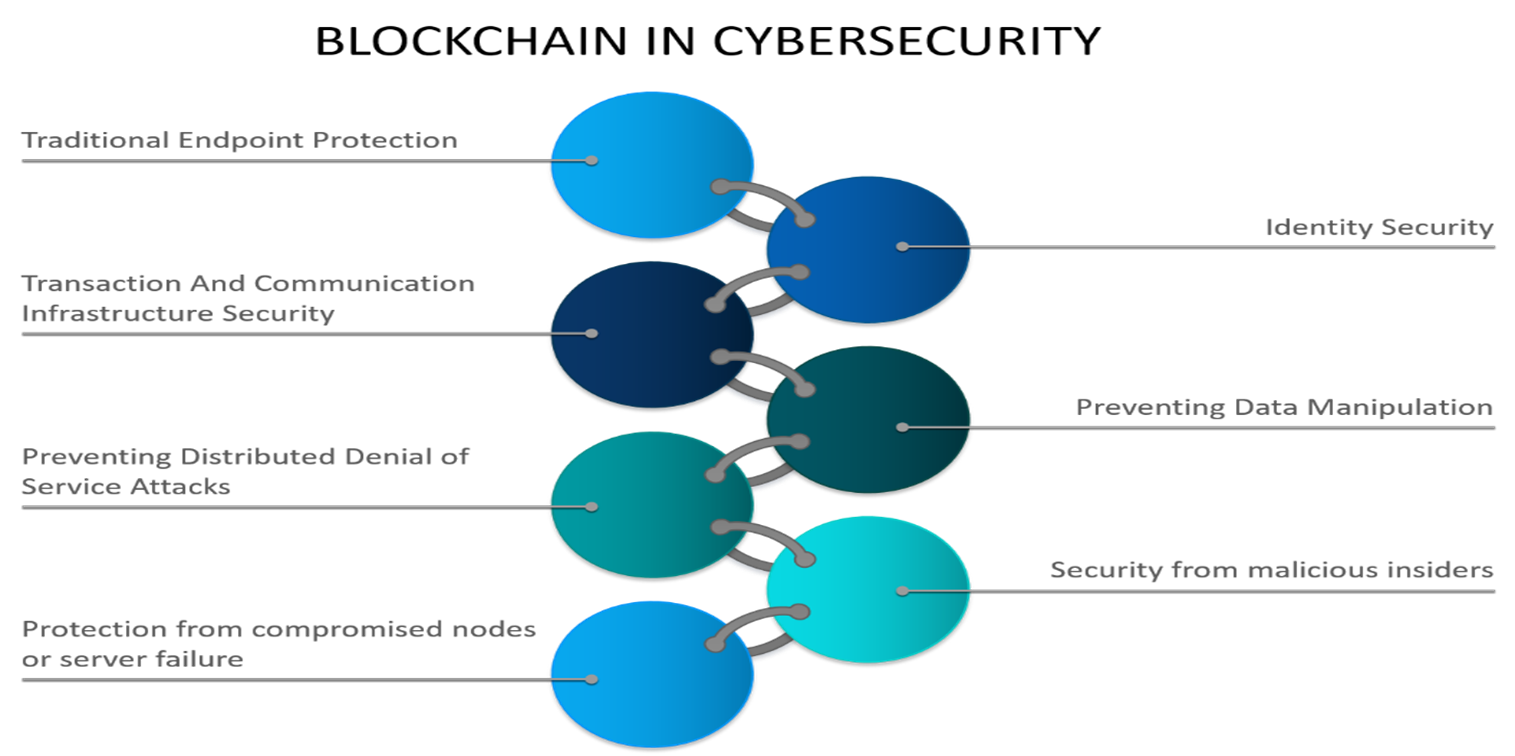
- Preventing DDoS: Currently, the DNS system relies on caching. This was confirmed on October 21, 2016 when millions of users across the US were cut off from major websites. The decentralized nature of Blockchain offers a solution to this problem.
How Does Blockchain Work to Improve Cybersecurity?

- Blockchain Chaining Process: The blocks in a Blockchain ledger are arranged in an order and composed together to execute transactions. A block consists of a header and a body. All the blocks are timestamped and signed by their creators. Blocks form a chain by defining a pointer to the previous block. The header contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, ensuring the immutability of the last block.
- Distributed Architecture: A distributed network is operationally resilient as it has no single point of failure. The risk is spread across many nodes, and an attack on any single node, or a few nodes would not compromise the ledger. Thus, decentralization makes the Blockchain network a less appealing target for ransomware attacks. In contrast, centrally stored information is more susceptible to attacks than information stored at multiple nodes.
How Does Blockchain Transform Cybersecurity?
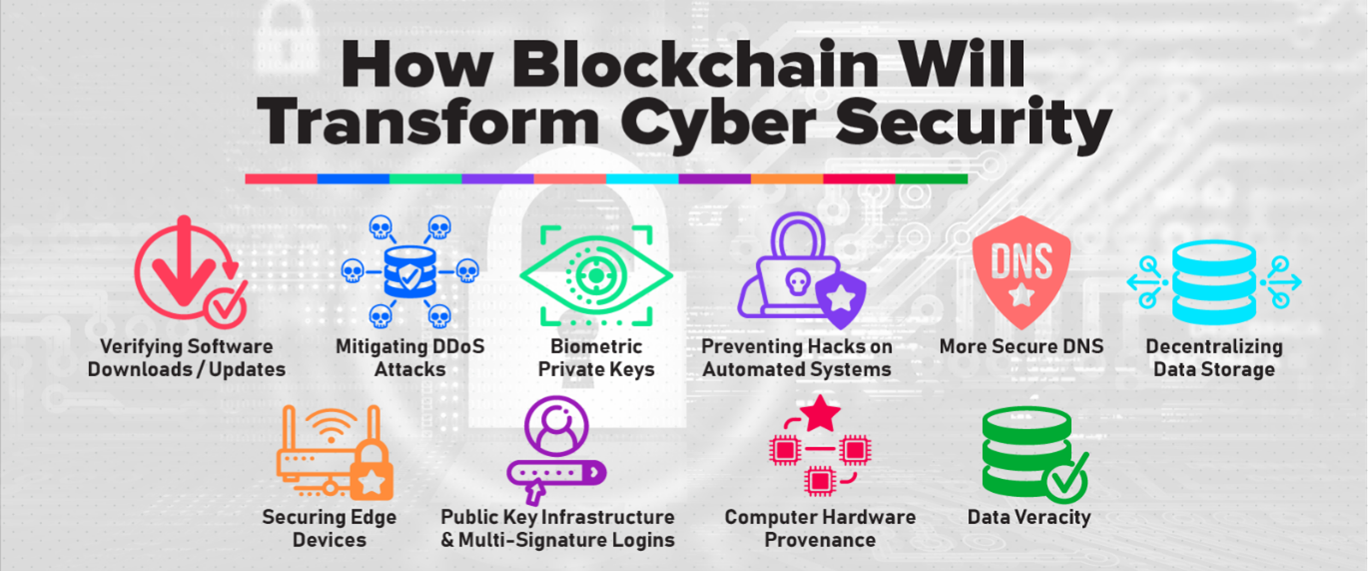
Blockchain's fundamental properties are decentralization and encryption. Each user has a private key to add blocks and make changes, and a public key to enable others to access the database so they can observe the modifications. Since Blockchain is a distributed system, obtaining user credentials to access systems is far more difficult, if not impossible, and to remove a whole Blockchain, each node must be manually destroyed.
As professionals study a range of use cases for blockchain technology, we can already identify the areas where cybersecurity would benefit greatly.
- Improve Identity and Access Management: The technology stores credentials on Blockchain in a decentralized manner, reducing system intrusion risks and access fraud as hackers need to exploit entry points to gain access to the data. We are fully aware that employee error is the primary cause of credential theft, which is centrally stored and managed.
- Track Changes: Blockchain aids in preventing unauthorized data changes and theft. Any modifications you make to Blockchain are irreversible, so you can’t go back and undo them. Additionally, updates or new data do not delete or replace old data; instead, they'll be recorded at the top of Blockchain with ownership and a timestamp, making them traceable in the event of an attack and enabling source tracking.
- Ensure Redundancy: A distributed Blockchain is continually present in many locations. As different computers maintain copies of Blockchain data, in the event of inadvertent or deliberate manipulation, you can locate the original data in other sources.
- Prevent Cyberattacks: DDoS attacks are frequent cyberattacks that try to overwhelm corporate systems with requests, crashing them and rendering them unusable. DDoS attacks are easy because parts of the DNS are stored centrally and are susceptible to attack and theft that can be used to destroy systems. The use of a decentralized Blockchain will minimize DNS theft and DDoS attacks. In addition, cyberattacks are promptly identified and prevented by preventing malicious data from entering the system because every block modification in the Blockchain must be confirmed with the other blocks.
Pros
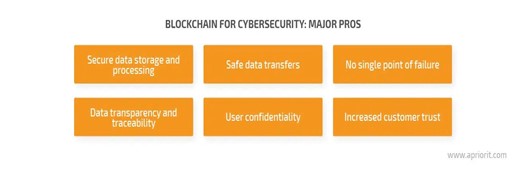
- User Confidentiality: The public key cryptography in a Blockchain network helps maintain the confidentiality of the users.
- Data Transparency and Traceability: The history of all these transactions is maintained so that they can be traced anytime. The transaction data is digitally signed by members of the Blockchain network to ensure transparency.
- Secure Data Storage and Processing: Blockchain’s key feature of immutability and records of any changes to the data help store the data safely and securely.
- No Single Point Failures: Blockchain systems are decentralized, so the failure of a single node does not affect the entire network. Thus, even during DDoS attacks, the system is not compromised due to the maintenance of multiple copies of ledgers. This advantage is not possible with private Blockchains.
- Safe Data Transfers: PKI in Blockchain maintains authentication during data transfers. Smart contracts help to automatically execute agreements between two parties during a transfer.
Cons
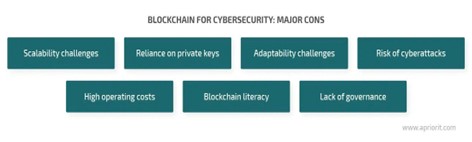
- Reliance on Private Keys: Blockchain relies heavily on private keys for encrypting data, but these private keys cannot be recovered once lost. This result in losing access to encrypted data forever.
- Adaptability and Scalability Challenges: Blockchain networks have a preset block volume and limits for transactions per second, so it very important to check the scalability of the network. Integrating Blockchain technology requires a complete replacement of existing systems, which is why companies may find this difficult.
- High Operating Costs: Blockchain requires high computing power and storage capabilities. This leads to higher costs compared to non-Blockchain applications.
- Lack of Governance: Blockchain concepts aren’t regulated globally yet. Regulations and frameworks need to be developed to maintain the governance in Blockchain applications.
- Blockchain Literacy: Learning Blockchain technology requires a profound knowledge of various development, programming languages, and other tools. Thus, despite numerous applications of Blockchain technology, there are not enough Blockchain developers available in the current scenario.
Conclusion
The Blockchain offers enough opportunities to maintain a high level of data security through reliable data encryption mechanisms, data integrity, network resilience, and scalability. As a result, switching from a traditional system to a Blockchain-based system can be beneficial for organizations in almost any industry.
Despite the mixed feelings about Blockchain, many industries have invested millions in Blockchain projects. With regards to cyber security, Blockchain should be a top priority for all industries handling data and for people who interact with data. With the maturity of the technology stack, Blockchain will become far more seamless to adopt as the main guard against cyber threats.
References
https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2022/03/04/how-blockchain-could-revolutionize-cybersecurity/?sh=4aa1db483a41
https://cybersecurityventures.com/hackerpocalypse-cybercrime-report-2016/#:~:text=Cybersecurity%20Ventures%20expects%20global%20cybercrime,%243%20trillion%20USD%20in%202015.
https://fintechmagazine.com/digital-payments/blockchain-technology-defi-security-hackers-market
https://www.wallarm.com/what/what-is-a-cyber-attack
https://www.business2community.com/cybersecurity/types-of-cyber-attacks-a-closer-look-at-common-threats-02352772
https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/the-cios-guide-to-blockchain
https://blockgeeks.com/blockchain-infographics/
https://medium.com/@ipspecialist/how-blockchain-technology-works-e6109c033034
https://www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/462-blockchain-cybersecurity-pros-cons?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=organic&utm_campaign=blog
https://www.xbrl.org/news/regulator-using-blockchain-for-cyber-security/
https://www.hcltech.com/blogs/will-blockchain-become-cyber-security-linchpin-digital-future
Blockchain & Cybersécurité:Partie II – Hemera Systems
https://www.techfunnel.com/information-technology/how-to-use-blockchain-technology-in-cyber-security/
https://www.bitdeal.net/blockchain-in-cybersecurity
About Encora
Fast-growing tech companies partner with Encora to outsource product development and drive growth. Contact us to learn more about our software engineering capabilities.